|
Dr. Juan (Jane) Cao (曹娟) Assistant Professor |
|
|
Affiliations:
Office TEL: +86 (0592) 2580683 |
|
Dr. Juan (Jane) Cao (曹娟) Assistant Professor |
|
|
Affiliations:
Office TEL: +86 (0592) 2580683 |
At present, Dr. Juan (Jane) Cao is an assistant professor at School of Mathematical Sciences, Xiamen University. She received her B.S. degree in Information and Computing Science from Department of Mathematics, Fuzhou University, in June 2004. She received her Ph.D. degree in Applied Mathematics from Zhejiang University under supervision of Prof. Guozhao Wang, in June 2009. During Oct. 2007 and Oct. 2008, she was a visiting scholar at Department of Computer Science, The State University of New York at Stony Brook (Stony Brook University), under supervision of Prof. Hong Qin.
(招收研究生) I am looking for intelligent, self-motivated, and dedicated graduate students. If you are interested in my research directions, please feel free to contact me.
Computer aided geometric design, Digital geometry processing for computer graphics
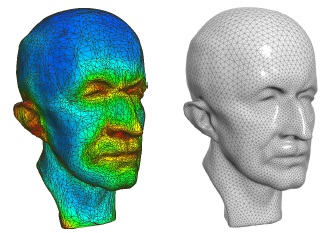 |
Isotropic Surface Remeshing Using Constrained Centroidal Delaunay Mesh Zhonggui Chen, Juan Cao*, Wenping Wang Computer Graphics Forum (Proc. Pacific Graphics), 31(7): 2077–2085, 2012 [Website] [Paper 10M] [SCI/JCR3] Abstract: We develop a novel isotropic remeshing method based on constrained centroidal Delaunay mesh (CCDM), a generalization of centroidal patch triangulation from 2D to mesh surface. Our method starts with resampling an input mesh with a vertex distribution according to a user-defined density function. The initial remeshing result is then progressively optimized by alternatively recovering the Delaunay mesh and moving each vertex to the centroid of its 1-ring neighborhood. The key to making such simple iterations work is an efficient optimization framework that combines both local and global optimization methods. |
 |
Spherical DCB-spline Surfaces with Hierarchical and
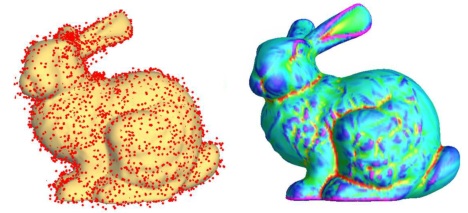
Adaptive knot Insertion Juan Cao*, Xin Li, Zhonggui Chen, Hong Qin IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 18(8): 1290-1303, 2012 [Website] [Paper 1.5M] [SCI/JCR2] Abstract: This paper develops a novel surface fitting scheme for automatically reconstructing a genus-0 object into a continuous parametric spline surface. A key contribution for making such a fitting method both practical and accurate is our spherical generalization of the Delaunay configuration B-spline (DCB-spline), a new non-tensor-product spline. In this framework, we efficiently compute Delaunay configurations on sphere by the union of two planar Delaunay configurations. Also, we develop a hierarchical and adaptive method that progressively improves the fitting quality by new knot-insertion strategies guided by surface geometry and fitting error. Within our framework, a genus-0 model can be converted to a single spherical spline representation whose root mean square error is tightly bounded within a user-specified tolerance. |
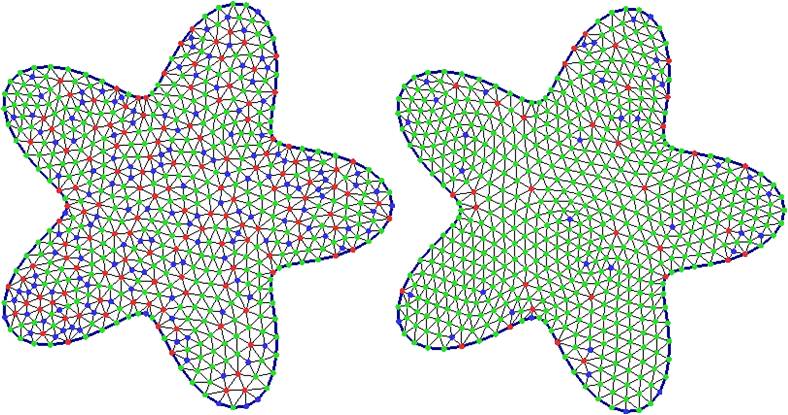 |
Topology Improvement for Constructing Optimal
Delaunay Triangulation Zhonggui Chen, Juan Cao*, Chenhui Yang Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 23(12), 1967-1974, 2011 [Paper 0.5M (in Chinese)] [EI] Abstract: Optimal Delaunay triangulation (ODT for short) is an optimization-based method for mesh generation. From the point of view of numerical optimization, the existing ODT method is a local optimization method, which is easy to get stuck at a bad local minimum corresponding to a mesh with low quality. In this paper, a topology improvement method is introduced into the ODT optimization procedure, which effectively enables ODT method to become unstuck from a poor local minimum and to proceed with optimization, therefore improves the qualities of generated meshes. The proposed topology improvement consists of only local operations of edge flipping, which is easy to implement. |
| Non-uniform B-spline Curves with Multiple Shape Parameters Juan Cao, Guozhao Wang Journal of Zhejiang University - Science C, 12(10):800-808, 2011 [Paper 0.5M] [SCI/JCR4] Abstract: We introduce a kind of shape-adjustable spline curves defined over a non-uniform knot sequence. These curves not only have the many valued properties of the usual non-uniform B-spline curves, but also are shape adjustable under fixed control polygons. Our method is based on the degree elevation of B-spline curves, where maximum degrees of freedom are added to a curve parameterized in terms of a non-uniform B-spline. We also discuss the geometric effect of the adjustment of shape parameters and propose practical shape modification algorithms, which are indispensable from the user’s perspective. |
|
| Surface reconstruction using bivariate simplex splines on Delaunay configurations Juan Cao, Xin Li, Guozhao Wang, Hong Qin Computers & Graphics, 33:341-350, 2009 [Paper 2M] [Talk 10M] [SCI/JCR4, EI] Abstract: Recently, a new bivariate simplex spline scheme based on Delaunay configuration has been introduced into the geometric computing community, and it defines a complete spline space that retains many attractive theoretic and computational properties. In this paper, we develop a novel shape modeling framework to reconstruct a closed surface of arbitrary topology based on this new spline scheme. Our framework takes a triangulated set of points, and by solving a linear least-square problem and iteratively refining parameter domains with newly added knots, we can finally obtain a continuous spline surface satisfying the requirement of a user-specified error tolerance. Unlike existing surface reconstruction methods based on triangular B-splines (or DMS splines), in which auxiliary knots must be explicitly added in advance to form a knot sequence for construction of each basis function, our new algorithm completely avoids this less-intuitive and labor-intensive knot generating procedure. We demonstrate the efficacy and effectiveness of our algorithm on real-world, scattered data sets for shape representation and computing. |
|
|
|
A Note on Class A Bézier Curves Juan Cao, Guozhao Wang Computer Aided Geometric Design, 25: 523–528, 2008 [Paper 0.5M] [SCI/JCR3] Abstract: The Class A Bézier curves presented in Farin (2006) were constructed by so-called Class A matrix, which are special matrices satisfying two appropriate conditions. The speciality of the Class A matrix causes the Class A Bézier to possess two properties, which are sufficient conditions for the proof of the curvature and torsion monotonicity. In this paper, we discover that, in Farin (2006), the conditions Class A matrix satisfied cannot guarantee one of the two properties of the Class A Bézier curves, then the proof of the curvature and torsion monotonicity becomes incomplete. Furthermore, we modified the conditions for the Class A matrices to complete the proof. |
|
|
The Structure of Uniform B-spline Curves with Parameters Juan Cao, Guozhao Wang Progress in Natural Science, 18: 303–308, 2008 [Paper 2M] [SCI/JCR4] Abstract: The shape-adjustable curve constructed by uniform B-spline basis function with parameter is an extension of uniform B-spline curve. In this paper, we study the relation between the uniform B-spline basis functions with parameter and the B-spline basis functions. Based on the degree elevation of B-spline, we extend the uniform B-spline basis functions with parameter to ones with multiple parameters. Examples show that the proposed basis functions provide more flexibility for curve design. |
2012.01 - 2014.12 National Science Foundation of China (No. 61100105) PI
2011.04 - 2014.03 National Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2011J05007) PI
2012.01 - 2014.12 National Science Foundation of China (No. 61100107) Co-PI
2012.01 - 2014.12 National Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2012J01291) Co-PI
Attending Academic Conferences
Visiting
Prof. Wenping Wang (The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong), Jun. - Sep. 2012
Prof. Jianmin Zheng (Nanyang Technological University, Singapore), Oct. 2011 - Feb. 2012
Single Variable Calculus, Multivariable Calculus, Linear Algebra